As artificial intelligence continues to advance and integrate into various industries, concerns are growing about the potential repercussions on the job market. A recent analysis highlights a troubling prediction: if most jobs were to be replaced by AI, unemployment could surge, leading to a significant decline in consumer purchasing power. This chain reaction may result in companies facing severe financial challenges, despite initial profitability from reduced labor costs. The scenario resembles a “tragedy of the commons,” where individual corporate gains could ultimately jeopardize the overall economic landscape. Experts suggest two possible pathways amid this upheaval: government intervention through measures like worldwide basic income or targeted job creation initiatives, or an unexpected surge in new employment opportunities arising from the AI revolution. As the future unfolds, the balance between innovation and societal well-being hangs in the balance, prompting urgent discussions about the best path forward.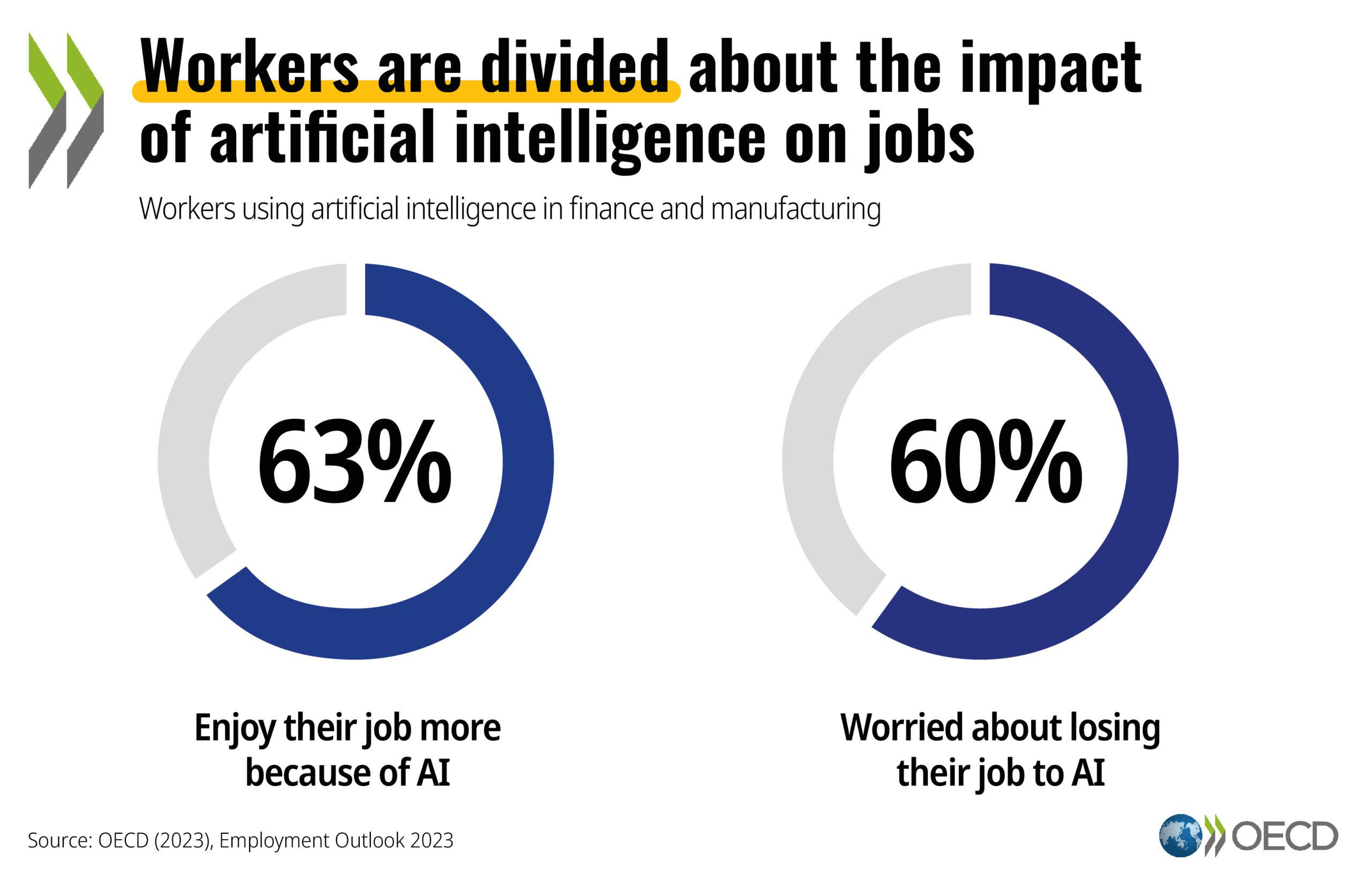
The Impact of AI on Employment and Economic Stability
As automation technology progresses, the workforce faces potential reshaping, where entire sectors might find customary roles obsolete. This evolution presents significant ramifications for economic stability, with the distribution of wealth becoming increasingly polarized. Factors to consider include:
- Shifts in skill requirements: The demand for high-skilled labor may soar, leaving low-skilled workers vulnerable to displacement.
- Regional disparities: Areas reliant on industries susceptible to automation might experience severe economic downturns.
- Consumer behavior changes: A workforce facing instability may lead to decreased spending, affecting businesses across sectors.
Moreover, the acceleration of AI integration into the economy raises questions on traditional employment models. The possibility of gig economies flourishing could emerge as a counterbalance to conventional career paths, yet this trend may lead to precarious job security for many. Innovative approaches are critical to adapt to this turbulence, such as:
- Investing in education and retraining: Empowering workers with skills to meet new market demands will be essential.
- Encouraging entrepreneurship: Supporting small businesses and startups could stimulate job creation in emerging sectors.
- Fostering collaboration between AI and humans: Developing hybrid models can offset the risks of automation while enhancing productivity.
Exploring Government Interventions: Universal Basic Income and Legislation
As the landscape of employment shifts dramatically due to the advent of AI technologies, discussions surrounding government interventions have gained momentum. One frequently enough-cited solution is Universal Basic Income (UBI), which proposes providing all citizens with a regular, unconditional sum of money to ensure their basic needs are met. This approach aims to stabilize consumer spending in an economy where a significant percentage of jobs may become automated. Advocates argue that UBI could serve as a safety net, promoting financial security and enabling individuals to pursue education or entrepreneurial endeavors, thereby facilitating a more adaptable workforce. The potential benefits include:
- Reduction of poverty: A basic income could help alleviate financial distress for those displaced by technology.
- Encouragement of innovation: With basic needs covered, individuals may feel more empowered to explore creative ventures without the anxiety of immediate financial survival.
- Boost in economic activity: Increased financial security tends to enhance consumer spending, vital for economic growth.
Alongside UBI, targeted legislation may play a crucial role in navigating the complexities of a future dominated by AI. Policymakers may need to consider a framework that seamlessly integrates technology into existing job markets while also focusing on job creation strategies in emerging fields. Key legislative measures could involve:
- Subsidizing industries: Providing financial support to sectors transitioning to AI, helping preserve jobs while facilitating modernization.
- Establishing regulations: Implementing guidelines for ethical AI development to protect workers’ rights and interests.
- Promoting social safety nets: Enhancing unemployment benefits and retraining programs to assist those affected by automation.
The Potential for Job Creation in an AI-Driven Future
In an era where AI is poised to redefine the workforce, the creation of new job opportunities could be a silver lining amidst the disruption. As businesses increasingly adopt AI technologies, they will also require a variety of roles to support, manage, and innovate these systems. These roles could range from technical positions, such as AI ethics officers and data scientists, to more nuanced positions focused on the human aspects of technology, like user experience designers and AI trainers. Companies may find that establishing a robust workforce with skills tailored to AI development becomes essential to maintain competitive advantage, underscoring the necessity for a collaborative relationship between humans and machines.
Moreover, the rise of AI might catalyze entirely new sectors that we cannot yet fully envision. The burgeoning fields of AI-enhanced healthcare, autonomous vehicle systems, and renewable energy solutions present vast potential for job creation. As more industries harness AI for efficiency and innovation, the demand for specialists who can navigate these new landscapes will likely surge. To maximize this potential, stakeholders must prioritize strategies such as:
- Fostering interdisciplinary collaboration: Encouraging partnerships between technology experts and industry leaders can drive holistic solutions.
- Advocating for policy reforms: Governments should establish frameworks that support innovation while safeguarding existing jobs.
- Promoting lifelong learning: Upskilling initiatives can ensure that the workforce remains adaptive, capable of evolving alongside AI advancements.
Navigating the Balance Between Profit and Workforce Sustainability
As companies increasingly turn to AI for operational efficiency, a growing tension arises between achieving profitability and maintaining a enduring workforce. Businesses may experience short-term gains from reduced labor costs, yet reliance on AI technologies could lead to long-term repercussions for employee retention and morale. Stakeholders must then prioritize strategies that enhance both profitability and job security, such as:
- Implementing fair compensation models: Ensuring that employees are adequately rewarded can foster loyalty and improve retention rates.
- Establishing clear communication: Engaging with employees about the integration of AI and its impact can mitigate fears and encourage collaboration.
- Encouraging employee involvement in AI development: Involving the workforce in discussions about AI solutions enhances their sense of ownership and security in their roles.
Moreover, prioritizing workforce sustainability could also become a competitive differentiator in the market. Companies that adopt socially responsible practices regarding their workforce may enjoy enhanced brand loyalty and attract customers who value ethical considerations. Efforts to innovate with a conscious eye towards worker implications can result in a more resilient business model overall. Companies should focus on initiatives such as:
- Building partnerships with educational institutions: Collaborating to create training programs that equip workers with skills necessary for a technology-driven landscape.
- Investing in employee mental health: Providing support systems for workers transitioning through changes instigated by AI can bolster productivity and job satisfaction.
- Developing community engagement initiatives: Encouraging participation in community-focused projects can strengthen the tie between the business and the societal fabric within which it operates.